Fat Burners: The Dark Side Of The 'Health' Industry
We don’t use fat burners, we never will. This article will explain why.

Bare Blends
2021-03-12

Weight loss supplements have become increasingly popular in recent years, leading to a new category of supplements - fat burners.
In a busy society, people are reaching for the quick fix more than ever. But you cannot outdo your fork. Nothing will ever take the place of good, solid hard work and determination, though many products have tried.
Fat burners are one such product.
If you've been with us for a while you will know that here at Bare Blends, we are backed by science. If you do your research properly, collate all the evidence and ask the right questions, the science does not lie.
We do not have a fat burner in our product range. We don’t use them, we never will. This article will explain a little more about why.
What are fat burners?
Fat burners are a classification of supplements that claim to increase the fat burning capacity of the body after consumption. These supplements contain ingredients that each have their own proposed mechanism of action and market the effect of fat burning, increased energy, weight loss and/or impaired fat absorption.
How do fat burners work?
Some fat burners claim to start the process of breaking down fat so that the body may use it as a fuel source, others say it is best used in conjunction with a healthy diet and exercise. One thing they all have in common is a high amount of stimulants. Fat burners are formulated to give you a boost in energy and suppress appetite.
Despite widespread use, to date there is very little evidence to support the efficacy of fat burners and more trials are needed to validate efficacy and safety.
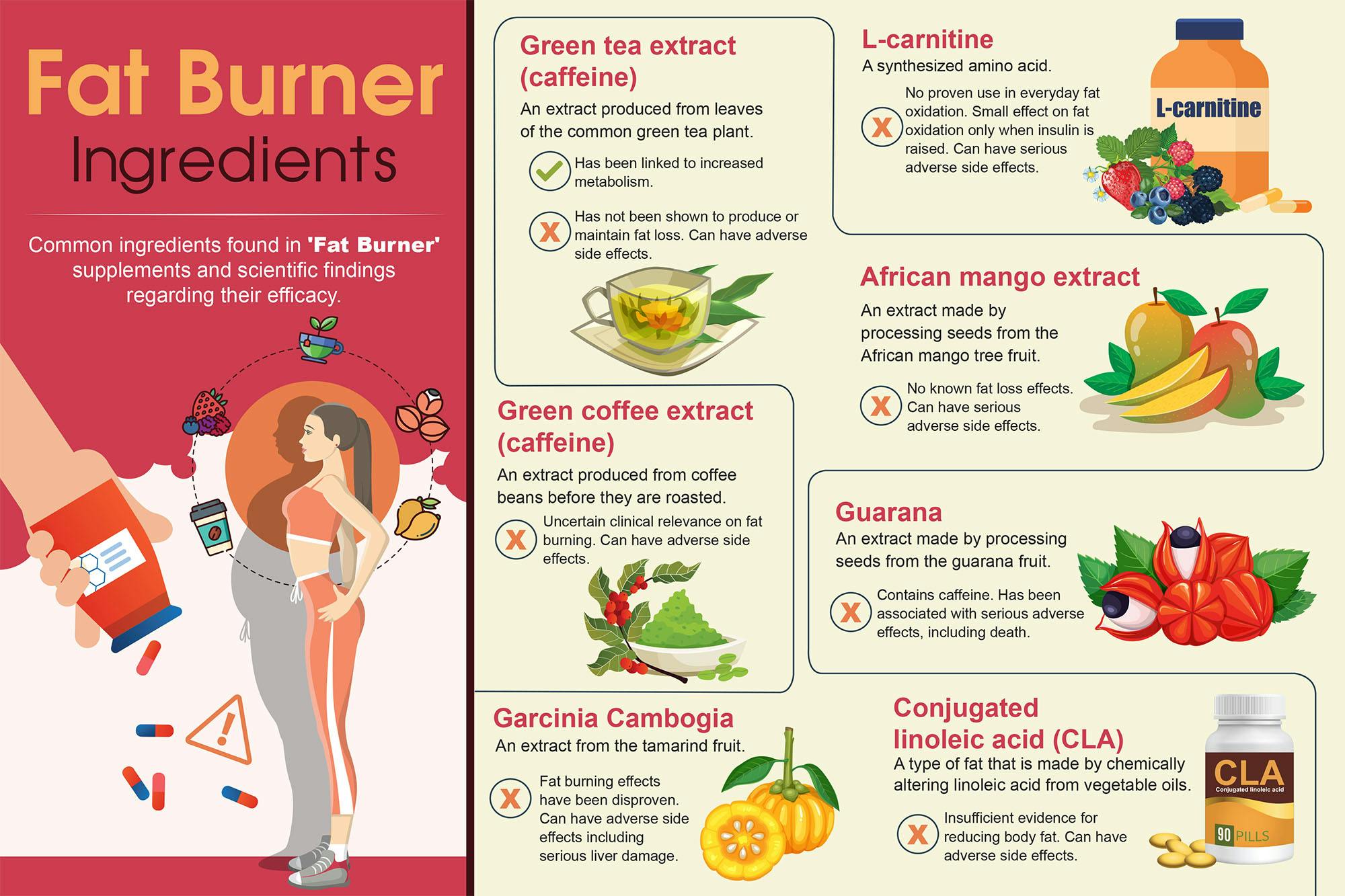
What's in fat burners?
Fat burners usually contain a range of ingredients - each is said to play a particular role in burning fat. The most common ingredients are as follows.
Caffeine
A diuretic with little to no clinical evidence on fat burning. The diuretic role of caffeine has the potential to be mistaken for fat burning or weight loss.
Green Coffee extract
Shown to have a very small impact on weight loss with uncertain clinical relevance on fat burning. Contains caffeine and has caffeine related side effects of nervousness, insomnia, stomach upset, nausea, increased heart rate, anxiety, among others.
Green tea extract
Has been linked to increased metabolism. Has not been shown to produce or maintain meaningful fat loss results, only very small changes that require further study.
L-carnitine
Similar chemical makeup to an amino acid. Its use in everyday fat oxidation has been disproven. It has a very small effect on fat oxidation only when insulin is raised by consuming large amounts of carbohydrate, which is counterproductive when trying to lose fat or weight.
African mango extract
Seems to be positively associated with weight loss, no known fat loss effects. Further studies required for efficacy on health outcomes.
Guarana
An alternative food containing caffeine. The Therapeutic Goods Administration (TGA) has warned against supplements with an undisclosed amount of caffeine after guarana was associated with adverse effects, including death.
Conjugated linoleic acid (CLA)
Clinical evidence on CLA reducing body fat is insufficient and not unanimous. Has been associated with negative effects on glucose metabolism and lipid profile.
Garcinia cambogia
An extract from the tamarind fruit. Associated with some nasty side effects, including liver issues, and disproven to have any effect in burning fat.
The caffeine-containing ingredients have shown to have minimal impact on fat burning. There is no regulation on the amount of caffeine that fat burning products contain, leaving this open to a broad range. Caffeine is also diuretic, prompting the body to lose water through urination which can lead to dehydration, this gives individuals the placebo effect of fat loss.
High intake of caffeine activates the sympathetic nervous system stimulating the adverse effects of caffeine, which can lead to endocrine imbalance and burn out of the adrenal and thyroid glands, anxiety, nervousness, diarrhoea, increased heart rate etc.

Are fat burners safe?
In 2018 the NSW Ministry of Health advised against products marketed as fat burners and urged the public to avoid them due to significant adverse effects.
In a 2018 study, Schmitz et al. reviewed 41121 cases of supplement adverse effects. Of these, fat burners and weight loss supplements produced the most frequent serious adverse effects (SAE’s), occurring most commonly in the cardiovascular, gastrointestinal, and nervous systems.
The main ingredients typically found in fat burners is caffeine. The inclusion of caffeine in a range of ‘health’ products has the potential to lead to unsafe intake of caffeine, TGA recommends knowing the caffeine dose prior to ingestion to avoid any serious adverse effects.
Caffeine is a central nervous system (CNS) stimulant, unnecessary prolonged high doses of caffeine have been linked to thyroid and adrenal burn out. Meaning high doses of caffeine have the potential to alter our hormonal balance which can lead to anxiety, depression, fatigue, drowsiness, irritability, lack of sleep among others.
Do fat burners actually work?
The data on this category of supplement is very limited and the studies that have been undertaken have not produced any significant results. More data is needed to determine not only the efficacy of these products but also safety and side effects.
The lack of clinical evidence with all ingredients of fat burners suggests that having a cup of green tea in the morning would be more effective on human health, with less destruction on the nervous system.
If you are considering taking supplements to aid a weight or fat loss journey, remember natural doesn't always mean safe.

How to lose fat safely
- Drink 2.5-3 litres of water daily
- Consume a healthy balanced diet
- Engage in regular physical exercise
- Yoga has been shown to reduce body mass index
- Avoid processed foods
- Increased muscle mass helps to burn more calories at rest
- Reduce sugar and alcohol intake
- Get a good amount of quality sleep
- Stress management techniques
Recommended foods to assist with weight loss
1. Protein
Protein consumption has a big effect on metabolism and satiety. This is thought to be because a higher protein diet results in higher thermic effect of food, increased secretion of satiety hormones and regulated release of glucose for balanced blood sugar levels. Protein also contains essential amino acids which help muscles to recover, burning more calories at rest, and improving your capacity for regular exercise.
Your body uses more energy to process protein (digesting and transporting nutrients) than it does for the same amount of carbohydrates. Nearly one-third of the calories in protein are burned in the process of digesting it, which helps to increase your metabolism.
2. Matcha Green Tea
Organic Japanese Matcha Green Tea is a potent source of green tea catechins which help to increase your body’s metabolism.
3. Chia Seeds
Soluble fibre in Organic Chia Seeds helps reduce insulin spikes in the body which keeps you feeling full for longer.
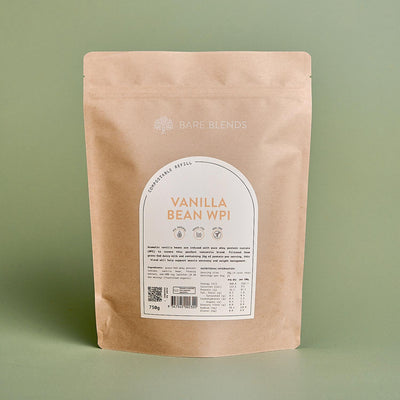

Vanilla Bean WPI
- Pure grass-fed whey protein isolate
- Aromatic vanilla bean
- Weight loss and lean muscle


Sources:
An evidence-based review of fat modifying supplemental weight loss productsMechanisms of caffeine-induced diuresis
The use of green coffee extract as a weight loss supplement: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomised clinical trials.
What are the effects of caffeine?
Green Tea
Fat burners: nutrition supplements that increase fat metabolism.
The Effects of Irvingia gabonensis Seed Extract Supplementation on Anthropometric and Cardiovascular Outcomes: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Australian Adverse Drug Reactions Bulletin
A review on effects of conjugated linoleic fatty acid (CLA) upon body composition and energetic metabolism.
An evidence-based review of fat modifying supplemental weight loss products.
The Effects of High Peripubertal Caffeine Exposure on the Adrenal Gland in Immature Male and Female Rats
Caffeine Withdrawal
Proposal to clarify that certain sports supplements should be regulated as therapeutic goods
A systematic review and meta-analysis on the effects of yoga on weight-related outcomes.
Protein-induced satiety: Effects and mechanisms of different proteins
Diet induced thermogenesis
Products in this post

Organic Japanese Matcha
